By Yitong Huang
With globally recognized brands from Toyota to Sony, Japan has emerged as one of the world’s largest exporters. With the third largest economy in the world, it should come as no surprise that Japan is also a major importer of goods and services. For more than four decades, Japan has been a trade powerhouse in the world economy, consistently ranking in the top five of exporters and importers.
An examination of Japan’s trading partners today reveals a robust trading relationship with the two most powerful economies in the world: China and the United States. Nearly one-third of Japan’s exports go to China and the United States (17.17% to China, and 14.25% to the United States). Meanwhile, more than a quarter of Japan’s imports come from both of those states: (18.71% from China and 8.35% from the United States). As is evident, China ranks as Japan’s top trade partner.
Japan’s leading exports to China include machinery, electronic equipment, vehicles, plastics, and medical equipment, among others. Its leading imports from China include electrical equipment, machinery, and apparel, among others. As for the United States, Japan’s top exports include vehicles, electronic equipment, and technical and medical equipment.
Below are Japan’s Top 5 Export Destinations with US$ Amount (2021)
- China (Mainland) – $163.59 Billion
- United States – $135.77 Billion
- South Korea – $52.50 Billion
- Taiwan – $54.45 Billion
- Hong Kong, China – $35.41 Billion
(AP Style for Country Names)
Below are Japan’s Top 5 Import Sources with US$ Amount (2021)
- China Mainland – $185.24 Billion
- United States – $82.66 Billion
- Australia – $51.64 Billion
- Taiwan – $33.57 Billion
- South Korea – $32.00 Billion
(AP Style for Country Names)
Below is a chart that breaks down Japan’s total exports and its top five destinations.
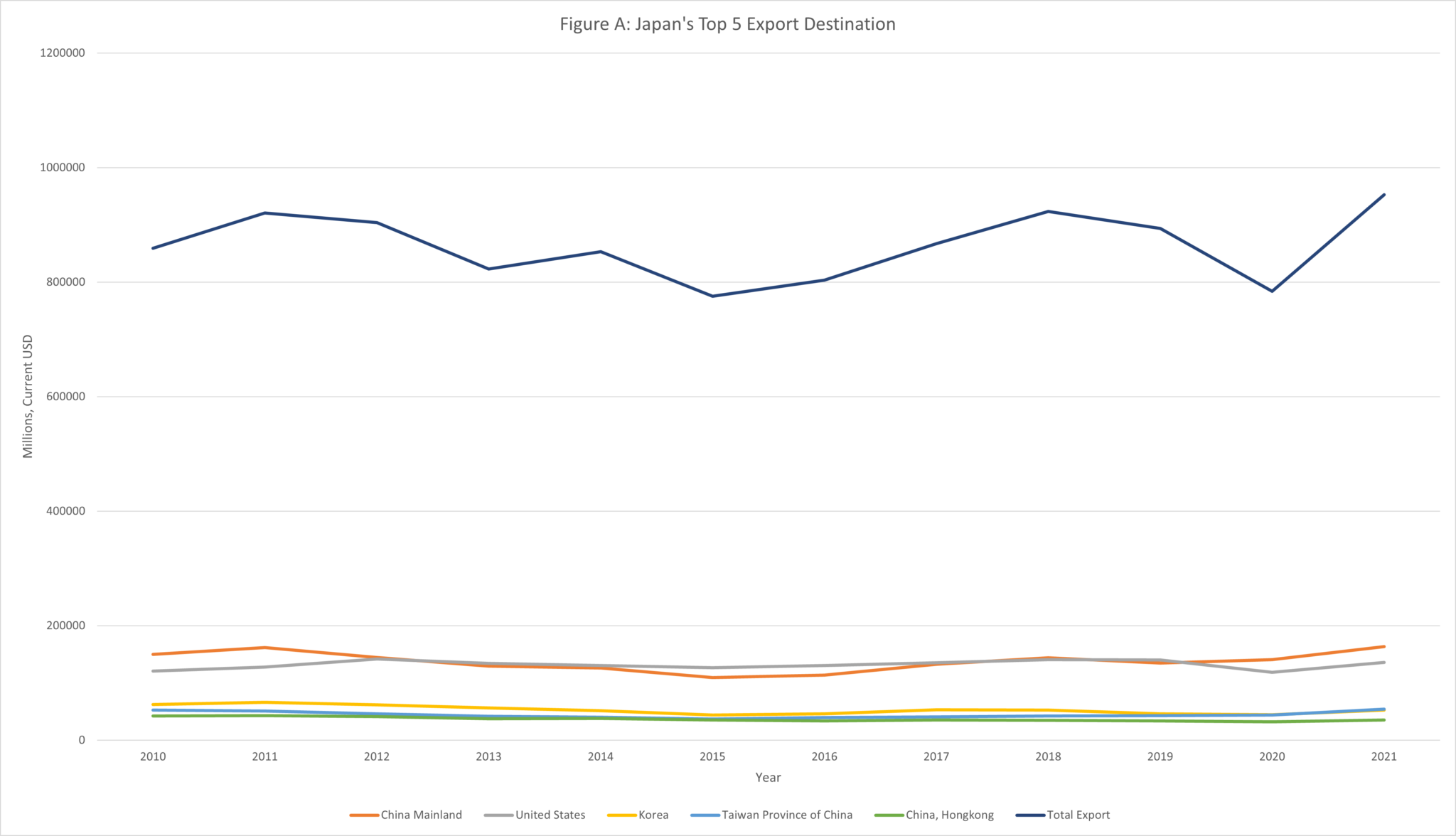
As can be seen in the chart above, Japan’s total exports witnessed a sharp recovery after a Covid-induced dip in 2020. Total exports now approach $1 trillion. Japan is the fourth largest exporter worldwide after China, the United States, and Germany, and just ahead of the United Kingdom. Forecasters see a modest 1.1% rise in Japan’s exports for 2022.
According to Daniel Workman, in an article on the site The World’s Top Exports, the following are: Japan’s top exports worldwide.
Japan’s Top Ten Exports by category (2021)
- Machinery including computers: US$147.1 billion (19.5% of total exports)
- Vehicles: $137.8 billion (18.2%)
- Electrical machinery, equipment: $117.9 billion (15.6%)
- Optical, technical, medical apparatus: $43 billion (5.7%)
- Iron, steel: $34.6 billion (4.6%)
- Plastics, plastic articles: $30.3 billion (4%)
- Organic chemicals: $18.3 billion (2.4%)
- Other chemical goods: $14.6 billion (1.9%)
- Gems, precious metals: $14.3 billion (1.9%)
- Copper: $12.9 billion (1.7%)
Japan’s top 10 exports accounted for roughly three-quarters (75.5%) of the overall value of its global shipments.
In a separate article, Workman notes the following companies as Japan’s top ten export powers
Japan’s Top Ten Export Companies
- Toyota Motor (car/truck makers):
- Sony (consumer electronics):
- Honda Motor (car/truck makers):
- Nissan Motor (car/truck makers):
- Hitachi (electronics):
- JXTG Holdings (oil, gas):
- Panasonic (consumer electronics):
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries (heavy equipment):
- Toshiba (IT, electronics):
- Nippon Steel (iron, steel):
The above list of Japan’s top exporting companies include several firms with global operations, notably the carmakers. They produce cars worldwide, and export them globally, though those figures are not counted as exports from Japan to the world.
Japan is also a major importer of goods and services, helping fuel global growth. The below chart lays out Japan’s total imports and its main import sources. The UAE and Saudi Arabia enter the list as major providers of petroleum. Japan is highly dependent on oil from the Middle East, accounting for more than 90% of their total demand.
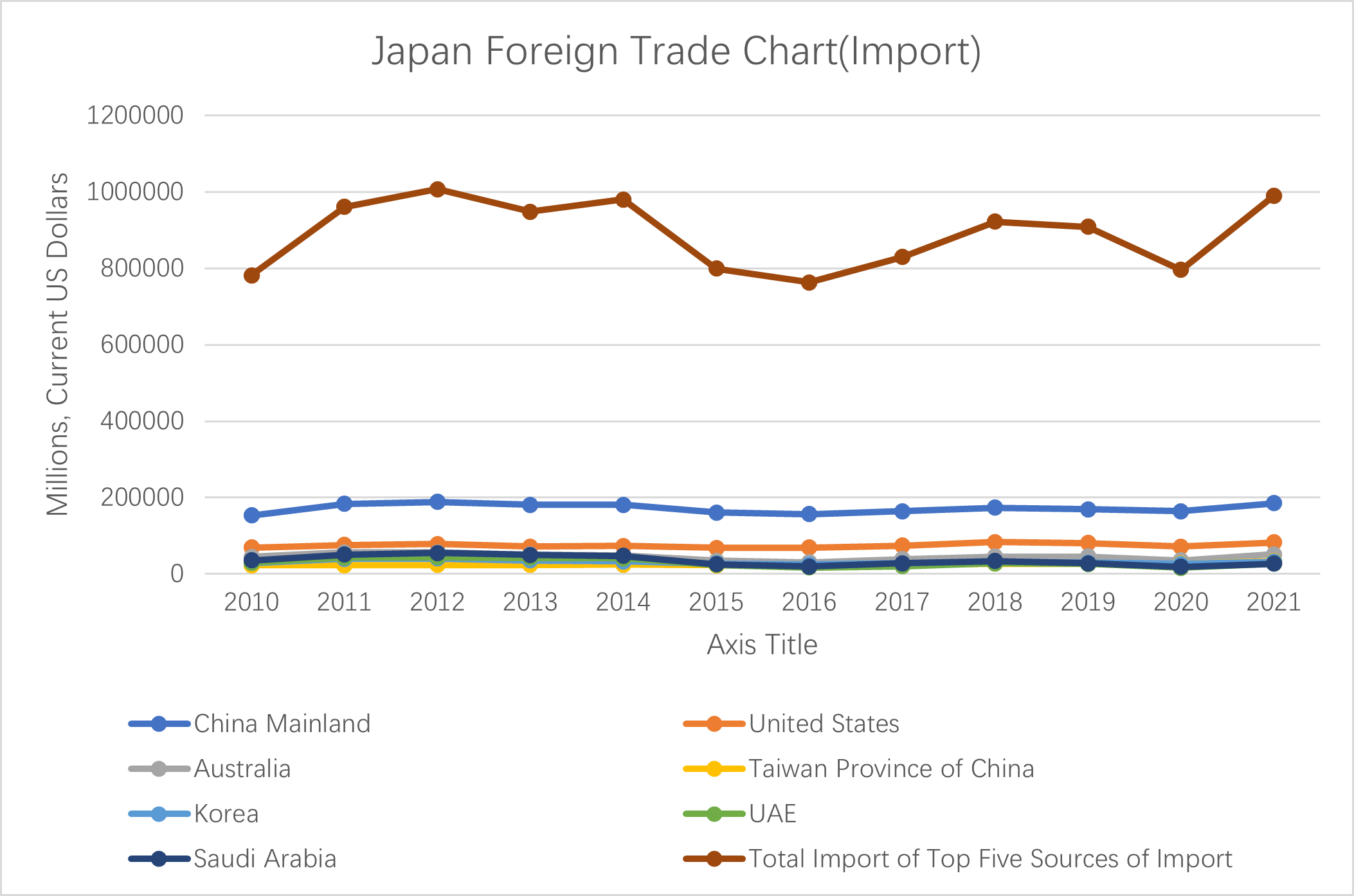
Japan is clearly a major trading nation. Its exports have ranked it in the top five of trading nations since the late 1970s, and its imports help fuel growth in Asia and among major oil and gas exporters in the Middle East. Despite geopolitical tensions with China and South Korea, both countries remain vital trade partners for Japan, with China emerging as Japan’s most important. The U.S still maintains a key place in Japan’s trade profile, and its heavy demand for fossil fuels will ensure that Saudi Arabia and the UAE remain key partners as well.


